* [jsscripting] Update openhab-js to 2.0.3 * [jsscripting] Update README Signed-off-by: Florian Hotze <florianh_dev@icloud.com>
JavaScript Scripting
This add-on provides support for JavaScript (ECMAScript 2021+) that can be used as a scripting language within automation rules.
Also included is openhab-js, a fairly high-level ES6 library to support automation in openHAB. It provides convenient access to common openHAB functionality within rules including items, things, actions, logging and more.
Configuration
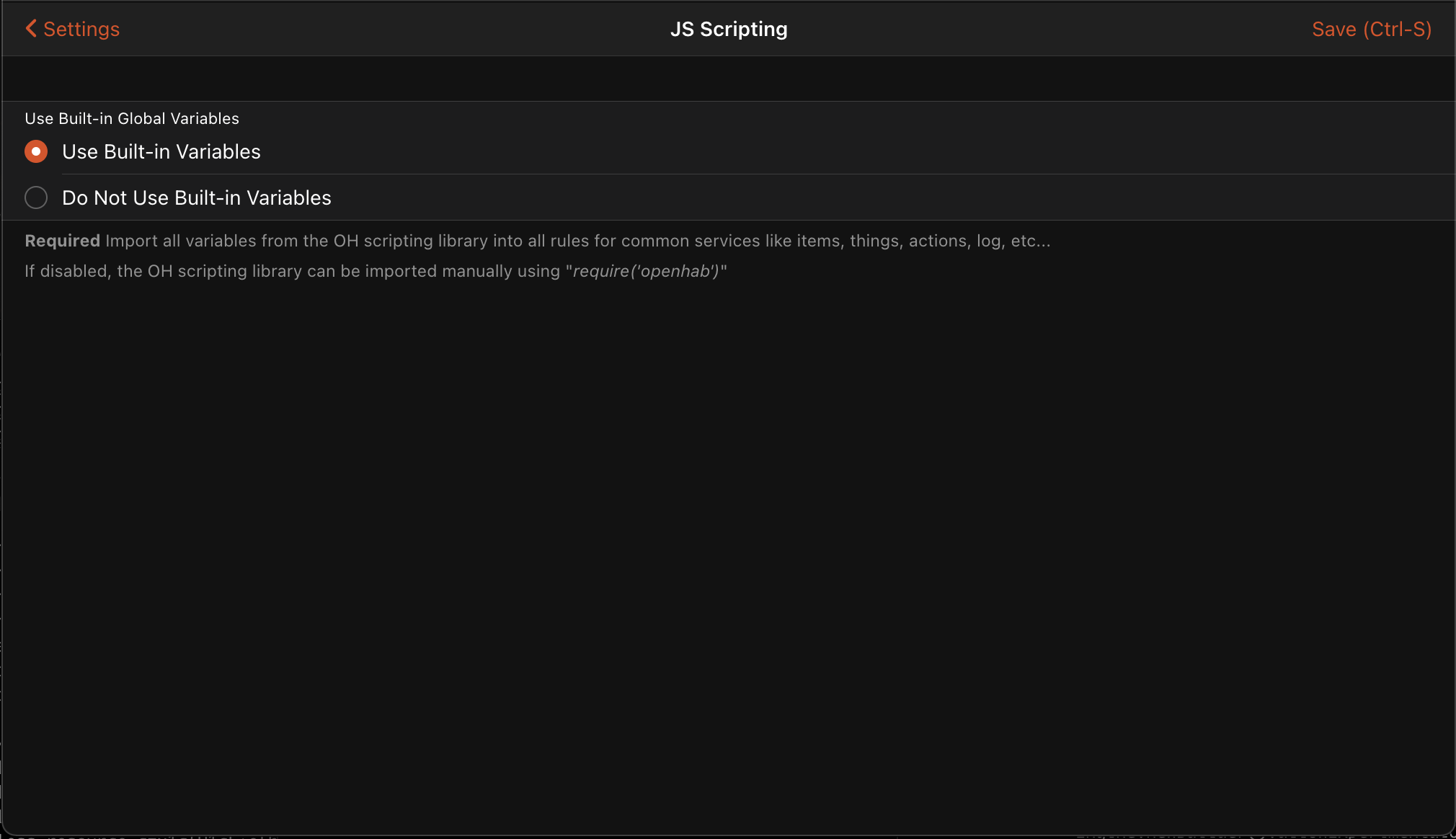
This add-on includes by default the openhab-js NPM library and exports its namespaces onto the global namespace.
This allows the use of items, actions, cache and other objects without the need to explicitly import using require().
This functionality can be disabled for users who prefer to manage their own imports via the add-on configuration options.
UI Based Rules
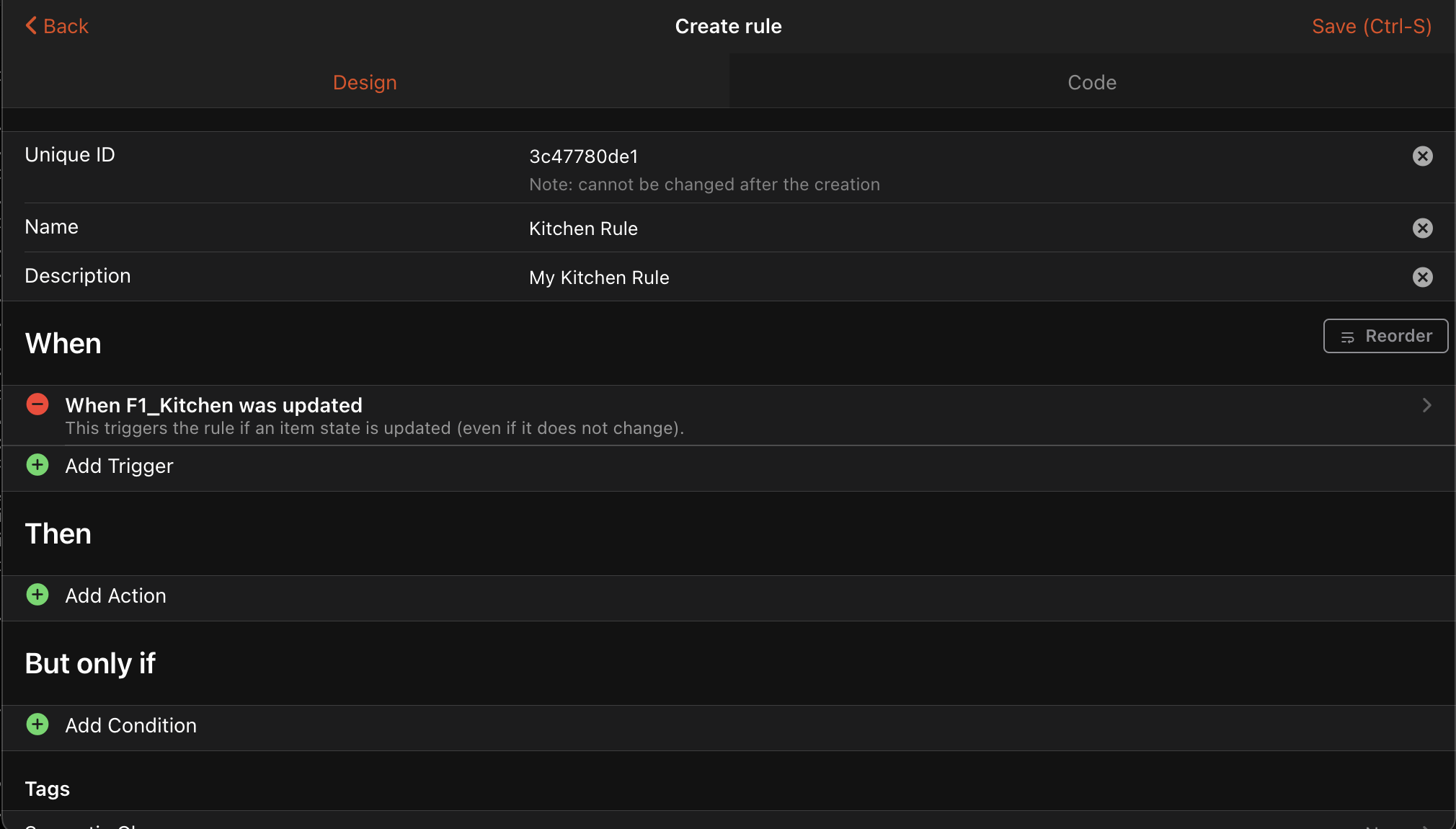
The quickest way to add rules is through the openHAB Web UI.
Advanced users, or users migrating scripts from existing systems may want to use File Based Rules for managing rules using files in the user configuration directory.
Adding Triggers
Using the openHAB UI, first create a new rule and set a trigger condition.
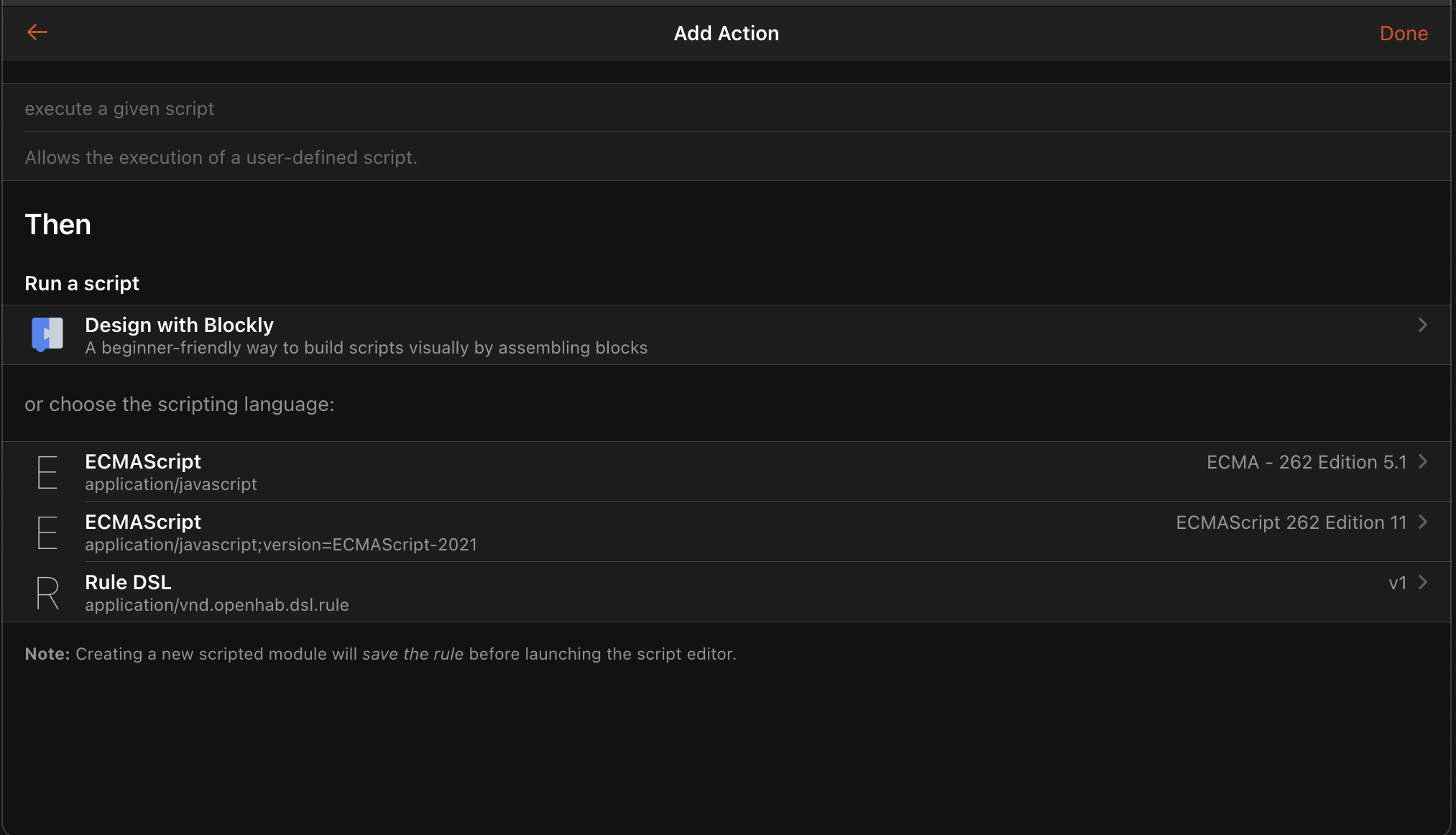
Adding Actions
Select "Add Action" and then select "Run Script" with "ECMAScript 262 Edition 11". It’s important this is "Edition 11" or higher, earlier versions will not work. This will bring up an empty script editor where you can enter your JavaScript.
You can now write rules using standard ES6 JavaScript along with the included openHAB standard library.
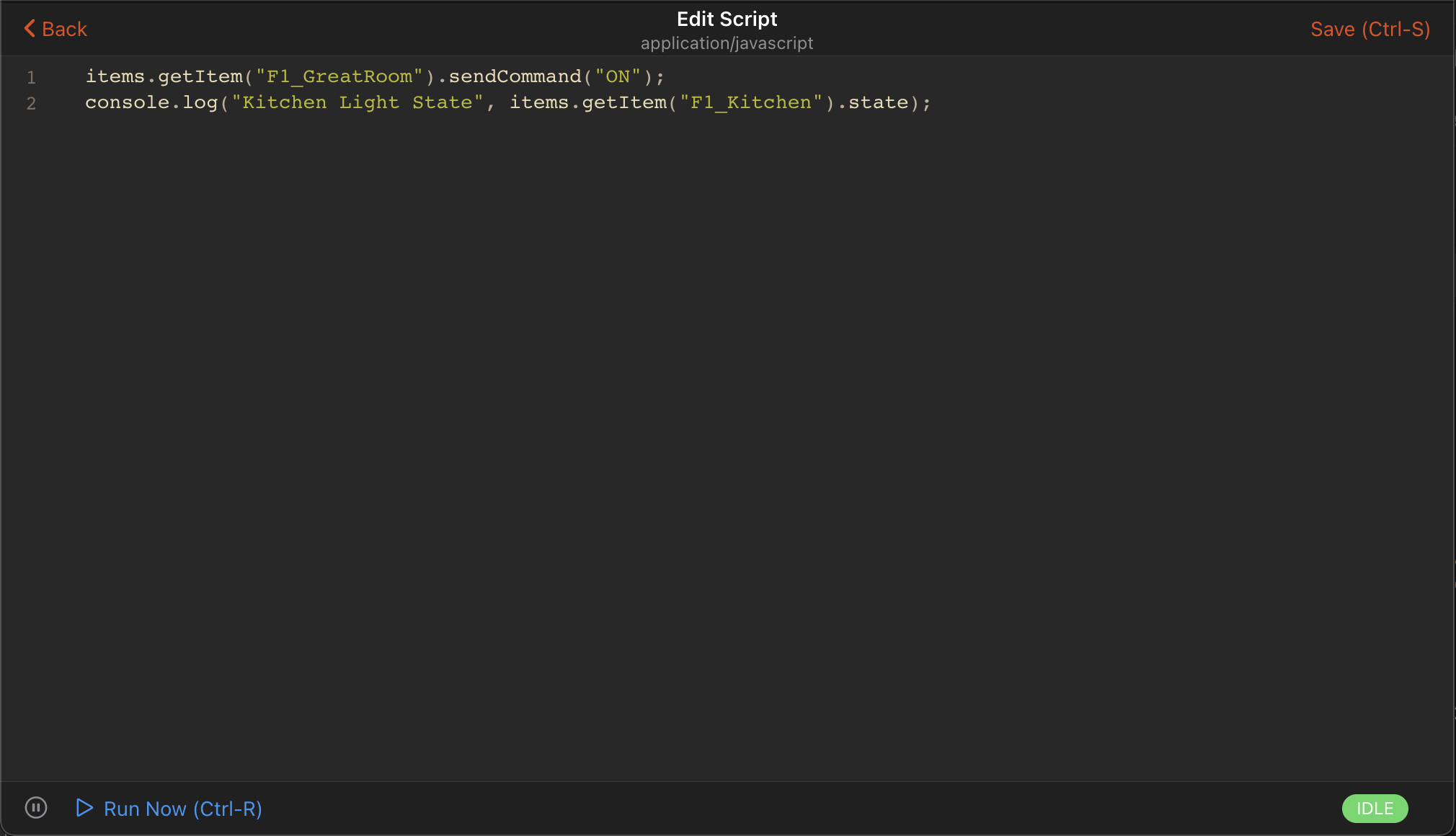
For example, turning a light on:
items.getItem("KitchenLight").sendCommand("ON");
console.log("Kitchen Light State", items.getItem("KitchenLight").state);
Sending a notification
actions.NotificationAction.sendNotification("romeo@montague.org", "Balcony door is open");
Querying the status of a thing
const thingStatusInfo = actions.Things.getThingStatusInfo("zwave:serial_zstick:512");
console.log("Thing status",thingStatusInfo.getStatus());
See openhab-js for a complete list of functionality.
UI Event Object
NOTE: Note that event object is different in UI based rules and file based rules! This section is only valid for UI based rules. If you use file based rules, refer to file based rules event object documentation.
When you use "Item event" as trigger (i.e. "[item] received a command", "[item] was updated", "[item] changed"), there is additional context available for the action in a variable called event.
This tables gives an overview over the event object for most common trigger types:
| Property Name | Type | Trigger Types | Description | Rules DSL Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
itemState |
sub-class of org.openhab.core.types.State | [item] changed, [item] was updated |
State that triggered event | triggeringItem.state |
oldItemState |
sub-class of org.openhab.core.types.State | [item] changed |
Previous state of Item or Group that triggered event | previousState |
itemCommand |
sub-class of org.openhab.core.types.Command | [item] received a command |
Command that triggered event | receivedCommand |
itemName |
string | all | Name of Item that triggered event | triggeringItem.name |
type |
string | all | Type of event that triggered event ("ItemStateEvent", "ItemStateChangedEvent", "ItemCommandEvent", ...) |
N/A |
Note that in UI based rules event.itemState, event.oldItemState, and event.itemCommand are Java types (not JavaScript), and care must be taken when comparing these with JavaScript types:
var { ON } = require("@runtime")
console.log(event.itemState == "ON") // WRONG. Java type does not equal with string, not even with "relaxed" equals (==) comparison
console.log(event.itemState.toString() == "ON") // OK. Comparing strings
console.log(event.itemState == ON) // OK. Comparing Java types
NOTE: Even with String items, simple comparison with == is not working as one would expect! See below example:
// Example assumes String item trigger
console.log(event.itemState == "test") // WRONG. Will always log "false"
console.log(event.itemState.toString() == "test") // OK
Scripting Basics
The openHAB JSScripting runtime attempts to provide a familiar environment to Javascript developers.
Require
Scripts may include standard NPM based libraries by using CommonJS require.
The library search will look in the path automation/js/node_modules in the user configuration directory.
Console
The JS Scripting binding supports the standard console object for logging.
Script debug logging is enabled by default at the INFO level, but can be configured using the console logging commands.
log:set DEBUG org.openhab.automation.script
The default logger name prefix is org.openhab.automation.script, this can be changed by assigning a new prefix to the loggerName property of the console.
console.loggerName = "custom"
Supported logging functions include:
console.log(obj1 [, obj2, ..., objN])console.info(obj1 [, obj2, ..., objN])console.warn(obj1 [, obj2, ..., objN])console.error(obj1 [, obj2, ..., objN])console.debug(obj1 [, obj2, ..., objN])console.trace(obj1 [, obj2, ..., objN])
Where obj1 ... objN is a list of JavaScript objects to output.
The string representations of each of these objects are appended together in the order listed and output.
See https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/console for more information about console logging.
Timers
SetTimeout
The global setTimeout() method sets a timer which executes a function or specified piece of code once the timer expires.
var ohTimer = setTimeout(callbackFunction, delay);
The global clearTimeout() method cancels a timeout previously established by calling setTimeout().
The openHAB implementation of setTimeout() differs from the HTML DOM API's setTimeout().
openHAB does not return the integer timeoutID as standard JS does, instead it returns an instance of openHAB Timer.
SetInterval
The setInterval() method repeatedly calls a function or executes a code snippet, with a fixed time delay between each call.
var ohIntervalTimer = setInterval(callbackFunction, delay);
The global clearInterval() method cancels a timed, repeating action which was previously established by a call to setInterval().
NOTE: Timers will not be canceled if a script is deleted or modified, it is up to the user to manage timers. See using the cache namespace as well as ScriptLoaded and ScriptUnLoaded for a convenient way of managing persisted objects, such as timers between reloads or deletions of scripts.
The openHAB implementation of setInterval() differs from the HTML DOM API's setInterval().
openHAB does not return the integer timeoutID as standard JS does, instead it returns an instance of openHAB Timer.
openHAB Timer
A native openHAB Timer instance has the following methods:
cancel(): Cancels the timer. ⇒boolean: true, if cancellation was successfulgetExecutionTime(): The scheduled execution time or null if timer was cancelled. ⇒time.ZonedDateTimeornullisActive(): Whether the scheduled execution is yet to happen. ⇒booleanisCancelled(): Whether the timer has been cancelled. ⇒booleanisRunning(): Whether the scheduled code is currently executed. ⇒booleanhasTerminated(): Whether the scheduled execution has already terminated. ⇒booleanreschedule(time.ZonedDateTime): Reschedules a timer to a new starting time. This can also be called after a timer has terminated, which will result in another execution of the same code. ⇒boolean: true, if rescheduling was successful
Examples:
var timer = setTimeout(() => { console.log('Timer expired.'); }, 10000); // Would log 'Timer expired.' in 10s.
if (timer.isActive()) console.log('Timer is waiting to execute.');
timer.cancel();
if (timer.isCancelled()) console.log('Timer has been cancelled.');
timer.reschedule(time.ZonedDateTime.now().plusSeconds(2)); // Logs 'Timer expired.' in 2s.
See openHAB JavaDoc - Timer for full API documentation.
Paths
For file based rules, scripts will be loaded from automation/js in the user configuration directory.
NPM libraries will be loaded from automation/js/node_modules in the user configuration directory.
Standard Library
Full documentation for the openHAB JavaScript library can be found at openhab-js.
Items
The items namespace allows interactions with openHAB items.
See openhab-js : items for full API documentation.
- items :
object- .getItem(name, nullIfMissing) ⇒
Item - .getItems() ⇒
Array.<Item> - .getItemsByTag(...tagNames) ⇒
Array.<Item> - .addItem(itemConfig)
- .removeItem(itemOrItemName) ⇒
Boolean - .replaceItem(itemConfig)
- .safeItemName(s) ⇒
String
- .getItem(name, nullIfMissing) ⇒
const item = items.getItem("KitchenLight");
console.log("Kitchen Light State", item.state);
getItem(name, nullIfMissing)
Calling getItem(...) returns an Item object with the following properties:
- Item :
object- .type ⇒
String - .name ⇒
String - .label ⇒
String - .history ⇒
ItemHistory - .state ⇒
String - .rawState ⇒
HostState - .members ⇒
Array.<Item> - .descendents ⇒
Array.<Item> - .isUninitialized ⇒
Boolean - .groupNames ⇒
Array.<String> - .tags ⇒
Array.<String> - .getMetadataValue(namespace) ⇒
String - .updateMetadataValue(namespace, value) ⇒
String - .upsertMetadataValue(namespace, value) ⇒
Boolean - .updateMetadataValues(namespaceToValues)
- .sendCommand(value)
- .sendCommandIfDifferent(value) ⇒
Boolean - .postUpdate(value)
- .addGroups(...groupNamesOrItems)
- .removeGroups(...groupNamesOrItems)
- .addTags(...tagNames)
- .removeTags(...tagNames)
- .type ⇒
const item = items.getItem("KitchenLight");
//send a ON command
item.sendCommand("ON");
//Post an update
item.postUpdate("OFF");
//Get state
console.log("KitchenLight state", item.state)
itemConfig
Calling addItem(itemConfig) or replaceItem(itemConfig) requires the itemConfig object with the following properties:
- itemConfig :
object- .type ⇒
String - .name ⇒
String - .label ⇒
String - .category (icon) ⇒
String - .groups ⇒
Array.<String> - .tags ⇒
Array.<String> - .channels ⇒
String|Object { channeluid: { config } } - .metadata ⇒
Object { namespace: value }|Object { namespace: { value: value , config: { config } } } - .giBaseType ⇒
String - .groupFunction ⇒
String
- .type ⇒
Note: .type and .name are required.
Basic UI and the mobile apps need metadata.stateDescription.config.pattern to render the state of an Item.
Example:
// more advanced example
items.replaceItem({
type: 'String',
name: 'Hallway_Light',
label: 'Hallway Light',
category: 'light',
groups: ['Hallway', 'Light'],
tags: ['Lightbulb'],
channels: {
'binding:thing:device:hallway#light': {},
'binding:thing:device:livingroom#light': {
profile: 'system:follow'
}
},
metadata: {
expire: '10m,command=1',
stateDescription: {
config: {
pattern: '%d%%',
options: '1=Red, 2=Green, 3=Blue'
}
}
}
});
// minimal example
items.replaceItem({
type: 'Switch',
name: 'MySwitch',
metadata: {
stateDescription: {
config: {
pattern: '%s'
}
}
}
});
See openhab-js : ItemConfig for full API documentation.
ItemHistory
Calling Item.history returns a ItemHistory object with the following functions:
- ItemHistory :
object- .averageBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .averageSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .changedBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
boolean - .changedSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
boolean - .deltaBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .deltaSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .deviationBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .deviationSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .evolutionRateBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .evolutionRateSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .historicState(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .lastUpdate(serviceId) ⇒
ZonedDateTime | null - .latestState(serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .maximumBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .maximumSince(timestamp,serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .minimumSince(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .minimumSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .persist(serviceId)
- .previousState(skipEqual, serviceId) ⇒
string | null - .sumBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .sumSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .updatedBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
boolean - .updatedSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
boolean - .varianceBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
number | null - .varianceSince(timestamp, serviceId) ⇒
number | null
- .averageBetween(begin, end, serviceId) ⇒
Note: serviceId is optional, if omitted, the default persistence service will be used.
var yesterday = new Date(new Date().getTime() - (24 * 60 * 60 * 1000));
var item = items.getItem('KitchenDimmer');
console.log('KitchenDimmer averageSince', item.history.averageSince(yesterday));
See openhab-js : ItemHistory for full API documentation.
Things
The Things namespace allows to interact with openHAB Things.
See openhab-js : things for full API documentation.
- things :
object- .getThing(uid, nullIfMissing) ⇒
Thing - .getThings() ⇒
Array.<Thing>
- .getThing(uid, nullIfMissing) ⇒
getThing(uid, nullIfMissing)
Calling getThing(...) returns a Thing object with the following properties:
- Thing :
object- .bridgeUID ⇒
String - .label ⇒
String - .location ⇒
String - .status ⇒
String - .statusInfo ⇒
String - .thingTypeUID ⇒
String - .uid ⇒
String - .isEnabled ⇒
Boolean - .setLabel(label)
- .setLocation(location)
- .setProperty(name, value)
- .setEnabled(enabled)
- .bridgeUID ⇒
const thing = things.getThing('astro:moon:home');
console.log('Thing label: ' + thing.label);
// Set Thing location
thing.setLocation('living room');
// Disable Thing
thing.setEnabled(false);
Actions
The actions namespace allows interactions with openHAB actions. The following are a list of standard actions.
Additional actions provided by user installed addons can be accessed using their common name on the actions name space
(example: actions.Pushsafer.pushsafer(...))
See openhab-js : actions for full API documentation and additional actions.
Audio Actions
See openhab-js : actions.Audio for complete documentation.
BusEvent
See openhab-js : actions.BusEvent for complete documentation.
Ephemeris Actions
See openhab-js : actions.Ephemeris for complete documentation.
Ephemeris is a way to determine what type of day today or a number of days before or after today is. For example, a way to determine if today is a weekend, a bank holiday, someone’s birthday, trash day, etc.
Additional information can be found on the Ephemeris Actions Docs as well as the Ephemeris JavaDoc.
// Example
let weekend = actions.Ephemeris.isWeekend();
Exec Actions
See openhab-js : actions.Exec for complete documentation.
Execute a command line.
// Execute command line.
actions.Exec.executeCommandLine('echo', 'Hello World!');
// Execute command line with timeout.
let Duration = Java.type('java.time.Duration');
actions.Exec.executeCommandLine(Duration.ofSeconds(20), 'echo', 'Hello World!');
// Get response from command line.
let response = actions.Exec.executeCommandLine('echo', 'Hello World!');
// Get response from command line with timeout.
response = actions.Exec.executeCommandLine(Duration.ofSeconds(20), 'echo', 'Hello World!');
HTTP Actions
See openhab-js : actions.HTTP for complete documentation.
// Example GET Request
var response = actions.HTTP.sendHttpGetRequest('<url>');
Replace <url> with the request url.
ScriptExecution Actions
See openhab-js : actions.ScriptExecution for complete documentation.
let now = time.ZonedDateTime.now();
// Function to run when the timer goes off.
function timerOver () {
console.info('The timer is over.');
}
// Create the Timer.
this.myTimer = actions.ScriptExecution.createTimer('My Timer', now.plusSeconds(10), timerOver);
// Cancel the timer.
this.myTimer.cancel();
// Check whether the timer is active. Returns true if the timer is active and will be executed as scheduled.
let active = this.myTimer.isActive();
// Reschedule the timer.
this.myTimer.reschedule(now.plusSeconds(5));
Semantics Actions
See openhab-js : actions.Semantics for complete documentation.
Things Actions
See openhab-js : actions.Things for complete documentation.
Voice Actions
See openhab-js : actions.Voice for complete documentation.
Cloud Notification Actions
Note: Optional action if openHAB Cloud Connector is installed.
Notification actions may be placed in rules to send alerts to mobile devices registered with an openHAB Cloud instance such as myopenHAB.org.
For available actions have a look at the Cloud Notification Actions Docs.
// Example
actions.NotificationAction.sendNotification('<email>', '<message>'); // to a single myopenHAB user identified by e-mail
actions.NotificationAction.sendBroadcastNotification('<message>'); // to all myopenHAB users
Replace <email> with the e-mail address of the user.
Replace <message> with the notification text.
Cache
The cache namespace provides a default cache that can be used to set and retrieve objects that will be persisted between reloads of scripts.
See openhab-js : cache for full API documentation.
- cache :
object- .get(key, defaultSupplier) ⇒
Object | null - .put(key, value) ⇒
Previous Object | null - .remove(key) ⇒
Previous Object | null - .exists(key) ⇒
boolean
- .get(key, defaultSupplier) ⇒
The defaultSupplier provided function will return a default value if a specified key is not already associated with a value.
Example (Get a previously set value with a default value (times = 0))
let counter = cache.get("counter", () => ({ "times": 0 }));
console.log("Count",counter.times++);
Example (Get a previously set object)
let counter = cache.get("counter");
if(counter == null){
counter = {times: 0};
cache.put("counter", counter);
}
console.log("Count",counter.times++);
Log
By default, the JS Scripting binding supports console logging like console.log() and console.debug() to the openHAB default log.
Additionally, scripts may create their own native openHAB logger using the log namespace.
let logger = log('my_logger');
//prints "Hello World!"
logger.debug("Hello {}!", "world");
Time
openHAB internally makes extensive use of the java.time package.
openHAB-JS exports the excellent JS-Joda library via the time namespace, which is a native JavaScript port of the same API standard used in Java for java.time.
Anywhere that a native Java ZonedDateTime or Duration is required, the runtime will automatically convert a JS-Joda ZonedDateTime or Duration to its Java counterpart.
The exported JS-Joda library is also extended with convenient functions relevant to openHAB usage.
Examples:
var now = time.ZonedDateTime.now();
var yesterday = time.ZonedDateTime.now().minusHours(24);
var item = items.getItem("Kitchen");
console.log("averageSince", item.history.averageSince(yesterday));
actions.Exec.executeCommandLine(time.Duration.ofSeconds(20), 'echo', 'Hello World!');
See JS-Joda for more examples and complete API usage.
time.toZDT()
There will be times when this automatic conversion is not available (for example when working with date times within a rule).
To ease having to deal with these cases a time.toZDT() function will accept almost any type that can be converted to a time.ZonedDateTime.
The following rules are used during the conversion:
| Argument Type | Rule | Examples |
|---|---|---|
null or undefined |
time.ZonedDateTime.now() |
time.toZDT(); |
time.ZonedDateTime |
passed through unmodified | |
java.time.ZonedDateTime |
converted to the time.ZonedDateTime equivalent |
|
JavaScript native Date |
converted to the equivalent time.ZonedDateTime using SYSTEM as the timezone |
|
number, bingint, java.lang.Number, DecimalType |
rounded to the nearest integer and added to now as milliseconds |
time.toZDT(1000); |
QuantityType |
if the units are Time, that time is added to now |
time.toZDT(item.getItem('MyTimeItem').rawState); |
items.Item or org.openhab.core.types.Item |
if the state is supported (see the Type rules in this table, e.g. DecimalType), the state is converted |
time.toZDT(items.getItem('MyItem')); |
String, java.lang.String, StringType |
parsed based on the following rules | |
RFC String (output from a Java ZonedDateTime.toString()) |
parsed | time.toZDT(new DateTimeType().getZonedDateTime().toString()); |
"HH:MM[:ss]" (24 hour time) |
today's date with the time indicated, seconds is optional | time.toZDT('13:45:12'); |
"kk:mm[:ss][ ]a" (12 hour time) |
today's date with the time indicated, the space between the time and am/pm and seconds are optional | time.toZDT('1:23:45 PM'); |
| Duration String | any duration string supported by time.Duration added to now(), see the docs for details |
time.toZDT('PT1H4M6.789S'); |
When a type or string that cannot be handled is encountered, an error is thrown.
toToday()
When you have a time.ZonedDateTime, a new toToday() method was added which will return a new time.ZonedDateTime with today's date but the original's time, accounting for DST changes.
For example, if the time was 13:45 and today was a DST changeover, the time will still be 13:45 instead of one hour off.
const alarm = items.getItem('Alarm');
alarm.postUpdate(time.toZDT(alarm).toToday());
isBetweenTimes(start, end)
Tests whether this time.ZonedDateTime is between the passed in start and end.
However, the function only compares the time portion of the three, ignoring the date portion.
The function takes into account times that span midnight.
start and end can be anything supported by time.toZDT().
Examples:
time.toZDT().isBetweenTimes('22:00', '05:00') // currently between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am
time.toZDT().isBetweenTimes(items.getItem('Sunset'), '11:30 PM') // is now between sunset and 11:30 PM?
time.toZDT(items.getItem('StartTime')).isBetweenTimes(time.toZDT(), 'PT1H'); // is the state of StartTime between now and one hour from now
isClose(zdt, maxDur)
Tests to see if the delta between the time.ZonedDateTime and the passed in time.ZonedDateTime is within the passed in time.Duration.
const timestamp = time.toZDT();
// do some stuff
if(timestamp.isClose(time.toZDT(), time.Duration.ofMillis(100))) {
// did "do some stuff" take longer than 100 msecs to run?
}
getMillisFromNow
This method on time.ZonedDateTime returns the milliseconds from now to the passed in time.ZonedDateTime.
const timestamp = time.ZonedDateTime.now().plusMinutes(5);
console.log(timestamp.getMillisFromNow());
Utils
openHAB internally is a Java program. openHAB-JS converts between Java and JavaScript data types and reverse.
See openhab-js : utils for full API documentation.
File Based Rules
The JS Scripting binding will load scripts from automation/js in the user configuration directory.
The system will automatically reload scripts when changes are detected to files.
Local variable state is not persisted among reloads, see using the cache for a convenient way to persist objects.
File based rules can be created in 2 different ways: using JSRule or the Rule Builder.
See openhab-js : rules for full API documentation.
JSRule
JSRules provides a simple, declarative syntax for defining rules that will be executed based on a trigger condition
const email = "juliet@capulet.org"
rules.JSRule({
name: "Balcony Lights ON at 5pm",
description: "Light will turn on when it's 5:00pm",
triggers: [triggers.GenericCronTrigger("0 0 17 * * ?")],
execute: (event) => {
items.getItem("BalconyLights").sendCommand("ON");
actions.NotificationAction.sendNotification(email, "Balcony lights are ON");
},
tags: ["Balcony", "Lights"],
id: "BalconyLightsOn"
});
Note: description, tags and id are optional.
Note: You can use the passed event object to get information about the trigger that triggered the rule.
See Event Object for documentation.
Multiple triggers can be added, some example triggers include:
triggers.ChannelEventTrigger('astro:sun:local:rise#event', 'START');
triggers.ItemStateChangeTrigger('my_item', 'OFF', 'ON');
triggers.ItemStateUpdateTrigger('my_item', 'OFF');
triggers.ItemCommandTrigger('my_item', 'OFF');
triggers.GroupStateChangeTrigger('my_group', 'OFF', 'ON');
triggers.GroupStateUpdateTrigger('my_group', 'OFF');
triggers.GroupCommandTrigger('my_group', 'OFF');
triggers.ThingStatusUpdateTrigger('some:thing:uuid','OFFLINE');
triggers.ThingStatusChangeTrigger('some:thing:uuid','ONLINE','OFFLINE');
triggers.SystemStartlevelTrigger(40) // Rules loaded
triggers.SystemStartlevelTrigger(50) // Rule engine started
triggers.SystemStartlevelTrigger(70) // User interfaces started
triggers.SystemStartlevelTrigger(80) // Things initialized
triggers.SystemStartlevelTrigger(100) // Startup Complete
triggers.GenericCronTrigger('0 30 16 * * ? *');
triggers.TimeOfDayTrigger('19:00');
triggers.DateTimeTrigger('MyDateTimeItem');
You can use null for a trigger parameter to skip its configuration.
See openhab-js : triggers in the API documentation for a full list of all triggers.
Rule Builder
The Rule Builder provides a convenient API to write rules in a high-level, readable style using a builder pattern.
Rules are started by calling rules.when() and can chain together triggers,
conditions and operations in the following pattern:
rules.when().triggerType()...if().conditionType().then().operationType()...build(name, description, tags, id);
Rule are completed by calling .build(name, description, tags, id) , all parameters are optional and reasonable defaults will be used if omitted.
nameString rule name - defaults generated namedescriptionString Rule description - defaults generated descriptiontagsArray of string tag names - defaults empty arrayidString id - defaults random UUID
A simple example of this would look like:
rules.when().item("F1_Light").changed().then().send("changed").toItem("F2_Light").build("My Rule", "My First Rule");
Operations and conditions can also optionally take functions:
rules.when().item("F1_light").changed().then(event => {
console.log(event);
}).build("Test Rule", "My Test Rule");
See Examples for further patterns.
Rule Builder Triggers
when()or().channel(channelName)Specifies a channel event as a source for the rule to fire..triggered(event)Trigger on a specific event name
.cron(cronExpression)Specifies a cron schedule for the rule to fire..item(itemName)Specifies an item as the source of changes to trigger a rule..for(duration).from(state).to(state).fromOff().toOn().receivedCommand().receivedUpdate()
.memberOf(groupName).for(duration).from(state).to(state).fromOff().toOn().receivedCommand().receivedUpdate()
.system().ruleEngineStarted().rulesLoaded().startupComplete().thingsInitialized().userInterfacesStarted().startLevel(level)
.thing(thingName)changed()updated()from(state)to(state)
Additionally all the above triggers have the following functions:
.if()or.if(fn)-> a rule condition.then()or.then(fn)-> a rule operation.or()-> a rule trigger (chain additional triggers)
Rule Builder Conditions
if(optionalFunction).stateOfItem(itemName)is(state)in(state...)
Rule Builder Operations
then(optionalFunction).build(name, description, tags, id).copyAndSendState().copyState().inGroup(groupName).postIt().postUpdate(state).send(command).sendIt().sendOff().sendOn().sendToggle()
Rule Builder Examples
// Basic rule, when the BedroomLight1 is changed, run a custom function
rules.when().item('BedroomLight1').changed().then(e => {
console.log("BedroomLight1 state", e.newState)
}).build();
// Turn on the kitchen light at SUNSET
rules.when().timeOfDay("SUNSET").then().sendOn().toItem("KitchenLight").build("Sunset Rule","turn on the kitchen light at SUNSET");
// Turn off the kitchen light at 9PM and tag rule
rules.when().cron("0 0 21 * * ?").then().sendOff().toItem("KitchenLight").build("9PM Rule", "turn off the kitchen light at 9PM", ["Tag1", "Tag2"]);
// Set the colour of the hall light to pink at 9PM, tag rule and use a custom ID
rules.when().cron("0 0 21 * * ?").then().send("300,100,100").toItem("HallLight").build("Pink Rule", "set the colour of the hall light to pink at 9PM", ["Tag1", "Tag2"], "MyCustomID");
// When the switch S1 status changes to ON, then turn on the HallLight
rules.when().item('S1').changed().toOn().then(sendOn().toItem('HallLight')).build("S1 Rule");
// When the HallLight colour changes pink, if the function fn returns true, then toggle the state of the OutsideLight
rules.when().item('HallLight').changed().to("300,100,100").if(fn).then().sendToggle().toItem('OutsideLight').build();
// And some rules which can be toggled by the items created in the 'gRules' Group:
// When the HallLight receives a command, send the same command to the KitchenLight
rules.when().item('HallLight').receivedCommand().then().sendIt().toItem('KitchenLight').build("Hall Light", "");
// When the HallLight is updated to ON, make sure that BedroomLight1 is set to the same state as the BedroomLight2
rules.when().item('HallLight').receivedUpdate().then().copyState().fromItem('BedroomLight1').toItem('BedroomLight2').build();
Event Object
NOTE: The event object is different in UI Based Rules and File Based Rules!
This section is only valid for File Based Rules.
If you use UI Based Rules, refer to UI based rules event object documentation.
When a rule is triggered, the script is provided the event instance that triggered it.
The specific data depends on the event type.
The event object provides some information about that trigger.
This tables gives an overview over the event object:
| Property Name | Trigger Types | Description | Rules DSL Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
oldState |
ItemStateChangeTrigger, GroupStateChangeTrigger |
Previous state of Item or Group that triggered event | previousState |
newState |
ItemStateChangeTrigger, GroupStateChangeTrigger |
New state of Item or Group that triggered event | N/A |
receivedState |
ItemStateUpdateTrigger, GroupStateUpdateTrigger |
State of Item that triggered event | triggeringItem.state |
receivedCommand |
ItemCommandTrigger, GroupCommandTrigger |
Command that triggered event | receivedCommand |
itemName |
Item****Trigger |
Name of Item that triggered event | triggeringItem.name |
receivedEvent |
ChannelEventTrigger |
Channel event that triggered event | N/A |
channelUID |
ChannelEventTrigger |
UID of channel that triggered event | N/A |
oldStatus |
ThingStatusChangeTrigger |
Previous state of Thing that triggered event | N/A |
newStatus |
ThingStatusChangeTrigger |
New state of Thing that triggered event | N/A |
status |
ThingStatusUpdateTrigger |
State of Thing that triggered event | N/A |
thingUID |
Thing****Trigger |
UID of Thing that triggered event | N/A |
eventType |
all except PWMTrigger, PIDTrigger, time triggers |
Type of event that triggered event (change, command, triggered, update) | N/A |
triggerType |
all except PWMTrigger, PIDTrigger, time triggers |
Type of trigger that triggered event | N/A |
All properties are typeof string.
NOTE:
Group****Triggers use the equivalent Item****Trigger as trigger for each member.
Time triggers do not provide any event instance, therefore no property is populated.
See openhab-js : EventObject for full API documentation.
Initialization hook: scriptLoaded
For file based scripts, this function will be called if found when the script is loaded.
scriptLoaded = function () {
console.log("script loaded");
loadedDate = Date.now();
};
Deinitialization hook: scriptUnloaded
For file based scripts, this function will be called if found when the script is unloaded.
scriptUnloaded = function () {
console.log("script unloaded");
// clean up rouge timers
clearInterval(timer);
};
Advanced Scripting
@runtime
One can access many useful utilities and types using require("@runtime"), e.g.
var { ON, OFF, QuantityType } = require("@runtime");
// Alternative, more verbose way to achieve the same:
//
// var runtime = require("@runtime");
//
// var ON = runtime.ON;
// var OFF = runtime.OFF;
// var QuantityType = runtime.QuantityType;
require("@runtime") also defines "services" such as items, things, rules, events, actions, ir, itemRegistry.
You can use these services for backwards compatibility purposes or ease migration from JSR223 scripts.
Generally speaking, you should prefer to use Standard Library provided by this library instead.